Ishan Shivanand, HOC’s Provider for Meditation Modalities
Ishan Shivanand is a world-renowned speaker, an acclaimed mental health researcher and a professor with expertise in non-pharmaceutical non-invasive meditative modalities and natural medicine. He is also the Founder of Yoga of Immortals (YOI) programs, San Francisco, CA. Director of Mental Health Initiatives of the Health Council Wheels Global Foundation, Virginia, and Visiting faculty of Integrative Yoga Therapy at Sri Jayadeva Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences and Research (SJICR) in Bangalore, India.
He has practiced meditation for over 25 years, including 15 years in full-time intensive training in monasteries in India.
His many contributions to the field of Integrative medicine include extensive travel to teach natural medicine, numerous research presentations and frequent publication in various peer-reviewed research journals. He has received several awards for his work on YOI and integrative medicine. He integrates lifestyle counseling, herbs, and various Yogic bodywork therapies individualized to the patient’s conditions. His area of expertise includes pain management, chronic health conditions, healthy weight management, digestive imbalances, women’s health, anti-aging therapies and preventative care. He believes in an integrative approach to health and wellness care.
Ishan Shivanand, ND

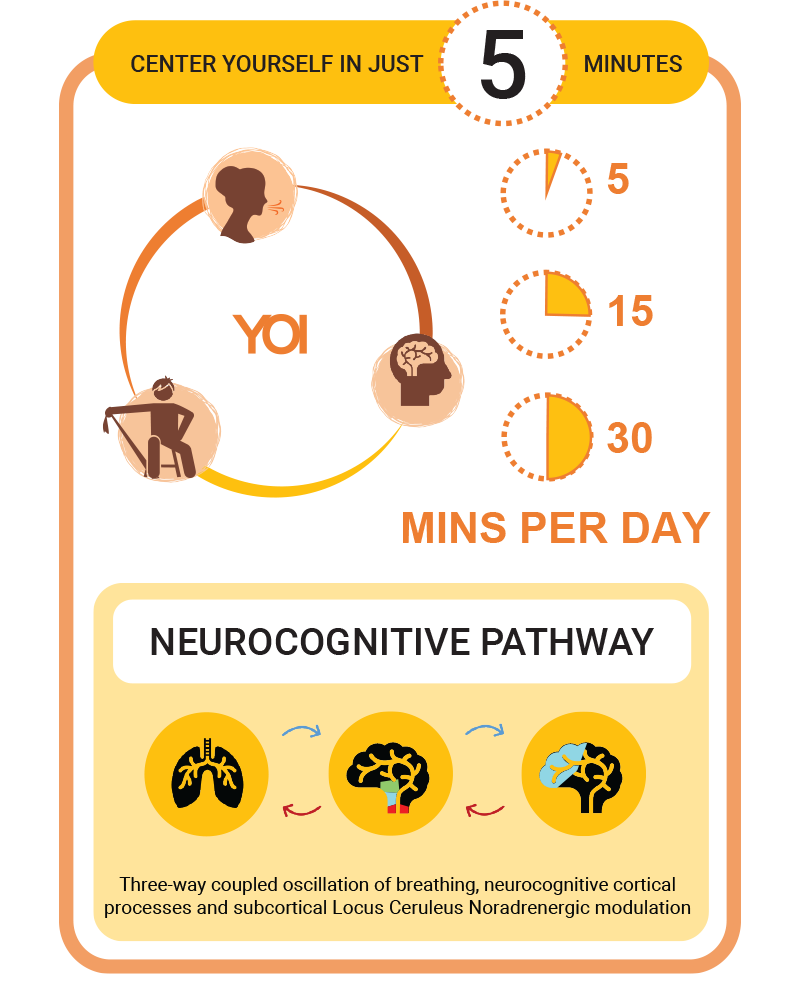
Ishan Shivanand, founder of Yoga of Immortals (YOI) https://yogaofimmortals.com is a mental health professor and researcher with specialization in meditative modalities. Scientifically validated YOI protocols are currently being actively integrated into diverse sectors, including Healthcare, Educational institutions, Sports, Military, and the Corporate world.
Life Resiliency Training With Ishan Shivanand
As hospice care providers, we face the challenge of supporting patients and their families through some of the most difficult times of their lives. It is important that we not only provide compassionate care but also develop the skills and tools we need to build resilience and manage the stress and emotional toll that this work can take. Life resilience training offers a holistic approach to building resilience that can be valuable for hospice staff as well as patients and their families. The training incorporates a range of techniques that can help individuals regulate their emotions, reduce stress and anxiety, and find meaning and purpose in their lives.
At the core of life resilience training are practices such as breathwork, awareness, mindfulness, visualization, and compassion. Breathwork can help us reduce anxiety and increase feelings of relaxation and calm. Awareness practices can help us become more aware of our thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations, allowing us to better regulate our responses to stress.
Mindfulness practices can help us stay present in the moment and find a sense of peace and acceptance. Visualization techniques can help us create positive outcomes and reduce stress and anxiety. Compassion practices involve cultivating feelings of kindness and empathy towards oneself and others, helping to reduce negative self-talk and improve relationships.
In addition to these practices, life resilience training may also incorporate conditioning and versatility exercises to help us develop physical and mental strength, endurance, and adaptability. Cultivating gratitude can also be an important aspect of life resilience training, helping us to focus on what we are grateful for in our lives and find meaning and purpose even in difficult times.
By learning and incorporating these techniques and practices into our work, we can build resilience and better manage the stress and emotional toll of hospice care. We can also model these practices for our patients and their families, helping them to find peace and comfort in their final days.
At hospice, we believe in providing compassionate care not only to our patients but also to our staff. By investing in our own well-being through life resilience training, we can better serve our patients and their families with empathy, strength, and resilience.

More About YOI
- Efficacy of YOI protocols have been published in leading international peer-reviewed medical journals. Results show 72% – 82% reduction in insomnia, anxiety, depression and 76% improvement in urinary incontinence and quality of life.
- Over the last decade, YOI protocols have benefited over one million individuals across 150 countries.
- Recognized for this groundbreaking work by governments across the globe; including India, the United States ofAmerica, United Kingdom, Mauritius, Kenya, South Africa, Singapore, Malaysia, and Canada.
- Additional international clientele includes – Robert Wood Johnson Medical Hospital (NJ, USA), Lenmed Hospital (South Africa), Thumbay Hospital (Dubai, UAE), Fraser Health (Canada), Ramsay Sime Darby Healthcare College (Selangor, Malaysia), LinkedIn, Google, Princeton (USA), International University of Vedic Wellness (FL, USA), SVNIT (Gujarat, India), Universiti Putra Malaysia (Malaysia)
Efficacy Of YOI Protocols
- Yoga of Immortals Intervention Reduces Symptoms of Depression, Insomnia and Anxiety
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.648029/full - Effectiveness of App-Based Yoga of Immortals (YOI) Intervention for Insomnia in Asian Population during Pandemic Restrictions
https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/11/5706/htm - Intervention on Depression and Insomnia Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic
https://anmrp.com/intervention-on-depression-and-insomnia-symptoms-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/ - Effectiveness of App- based Yoga of Immortals Intervention in Urinary Incontinence
https://www.auajournals.org/doi/10.1097/JU.0000000000002082.18 - Reductions in Anxiety, Depression and Insomnia in Health Care Workers Using a Nonpharmaceutical Intervention
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.983165/abstract - Online Yoga Instruction Improves Resilience in Athletes During the COVID -19 Pandemic (article under review)
https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202208.0549/v1